Ammonia is a commonly used industrial chemical, serving various purposes across different sectors. The potential dangers associated with ammonia gas leaks necessitate a thorough understanding of the risks and implementation of stringent safety measures. In this post, we explore the general dangers of ammonia gas leaks and critical safety precautions to help protect people, property, and the environment.
Common Industrial Uses of Ammonia Gas
While multiple industries use ammonia gas (NH3), the most common application is in the manufacturing of fertilizer for the agriculture industry. Fertilizer manufacturing accounts for around 80 percent of ammonia gas use in the United States. Ammonia is also a common coolant in large-scale refrigeration systems. Common applications of NH3 in the food industry include:
- Beverage bottling
- Meatpacking
- Dairies and creameries
- Produce
Other applications of ammonia gas span a wide range of industrial applications. Some of these secondary uses include:
- Stack gas emission control systems
- Chemical production
- Pharmaceuticals and cosmetics
- Oil production
- Cold storage warehouses
Regardless of the application, ammonia gas presents hazards for humans and the environment should the gas leak. It is important to understand the hazards posed by ammonia and to be proactive about monitoring for potential leaks.
The Hazards of Ammonia Gas
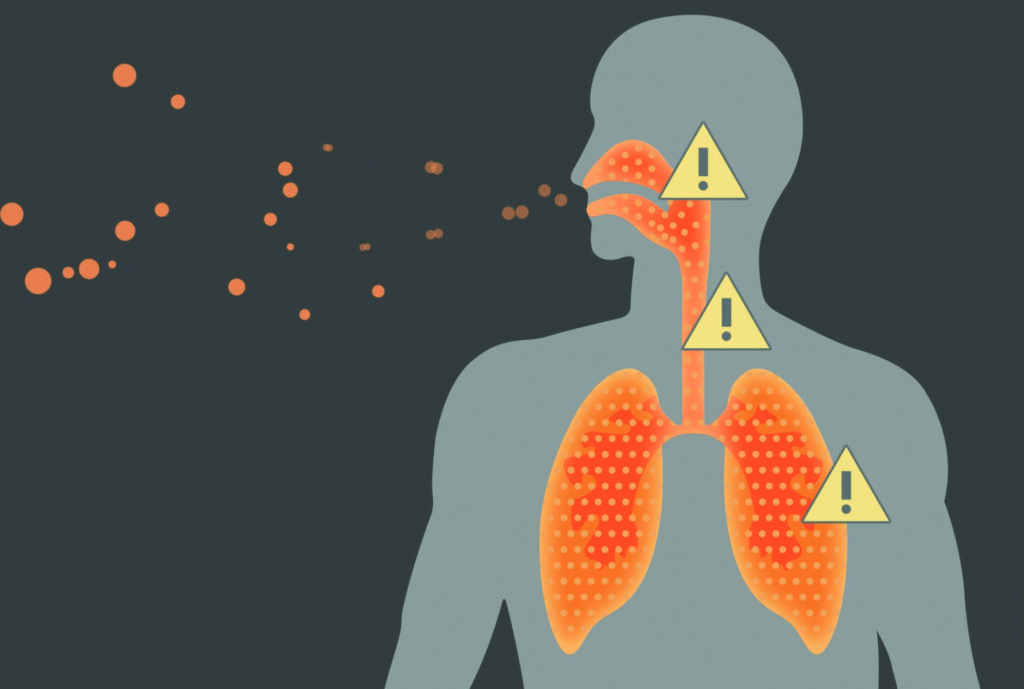
Ammonia is a colorless gas with a pungent odor, and exposure to it poses significant health risks. The dangers of ammonia gas include:
- Respiratory Irritation: Inhaling ammonia vapors can irritate the respiratory system, causing coughing, shortness of breath, and potentially severe respiratory distress.
- Eye Irritation and Damage: Eye contact with ammonia can cause irritation and burning sensations. Prolonged exposure may result in corneal burns and permanent eye damage.
- Skin Burns and Irritation: Ammonia is corrosive and can cause burns and irritation. Direct skin exposure may lead to chemical burns and dermatitis.
Toxicity: Ammonia is toxic. Exposure to high concentrations can affect the central nervous system, causing symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and in extreme cases, unconsciousness potentially resulting in fatal exposure
Exposure limits for ammonia are set by various health and safety organizations to protect workers and the general population. These limits are typically defined as permissible exposure limits (PELs) and short-term exposure limits (STELs). It’s important to note that these limits can vary between countries and organizations. Here are some commonly referenced exposure limits for ammonia:
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA – United States):
- Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL): 25 parts per million (ppm) as an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA).
- Short-Term Exposure Limit (STEL): 35 ppm for a 15-minute TWA.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH – United States):
- Recommended Exposure Limit (REL): 25 ppm as a 10-hour TWA.
- Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health (IDLH): 300 ppm. Exposure at or above this level is considered immediately dangerous to life or health.
- Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety (CCOHS)
- 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA): 25 ppm
- Short-Term Exposure Limit (STEL): 35 ppm.
Safety Measures and Best Practices
A robust safety blueprint is necessary to prevent adverse impacts to people and the environment should an ammonia leak occur. A multi-strategy safety solution approach can help lower the risk of injury to people, facilities, and environmental impacts. Below are some critical safety precautions that should be considered:
1. Fixed Gas Detection Systems
A fixed gas detection system can play a crucial role in mitigating risks associated with ammonia gas releases. These systems are designed to monitor the air for the presence of specific gases and provide early warnings in the event of a leak. Here’s how a fixed gas detection system can help detect and mitigate impacts from potential ammonia gas leaks:
- Early Detection and Warning:
- One of the primary advantages of a fixed gas detection system is its ability to detect ammonia leaks at an early stage.
- Sophisticated sensors continuously monitor the air, providing real-time data on gas concentrations.
- The system triggers alarms if a leak occurs, alerting personnel to the presence of the gas.
- Swift Response and Containment:
- Early detection enables an early response to an ammonia leak, allowing personnel to take immediate action.
- Emergency response procedures can be activated quickly, minimizing the duration and extent of ammonia exposure.
- Preventing Escalation:
- Early detection and warnings help prevent small leaks from escalating into more significant incidents.
- Rapid identification and intervention can prevent the release of large quantities of ammonia, reducing the potential for widespread exposure and environmental impacts.
- Protecting Personnel and Assets:
- The primary objective of a fixed gas detection system is to protect the safety of personnel and assets in the vicinity of the ammonia source.
- Alarms and warnings allow workers to evacuate promptly, reducing the risk of inhalation and other health hazards associated with ammonia exposure.
- Compliance with Regulations:
- Many industries are subject to regulations and standards regarding the use and handling of hazardous substances like ammonia.
- A fixed gas detection system helps facilities comply with safety regulations by providing a proactive means of monitoring and managing gas releases.
- Reduced Environmental Impact:
- In addition to human safety, timely detection and response also helps minimize environmental impacts of ammonia releases.
- Helping prevent ammonia from entering the atmosphere or water systems reduces potential harm to ecosystems.
- System Integration and Data Logging:
- Fixed gas detection systems often allow integration with other safety systems and data logging capabilities.
- Integration enables a more comprehensive approach to safety, and data logging provides valuable information for post-incident analysis and continuous improvement.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Workers handling or working in areas where ammonia is present should wear appropriate PPE, including portable gas detectors, goggles, face shields, gloves, and respiratory protection.
3. Ventilation Systems
Proper ventilation is crucial in spaces where ammonia is used or stored. Adequate ventilation helps disperse any leaked gas, preventing its accumulation and mitigating risks of high-concentration exposure.
4. Emergency Response Plans
Facilities utilizing ammonia should have well-defined emergency response plans in place. This includes evacuation procedures, first aid measures, and coordination with emergency services.
5. Training Programs
Comprehensive training for personnel on the proper handling, storage, and emergency response procedures related to ammonia is crucial. Regular drills ensure workers are well-prepared to respond effectively in the event of a leak.
Understanding the dangers associated with ammonia gas leaks is essential for ensuring the safety of both workers and the surrounding community. By implementing strict safety measures, including the use of fixed gas detection systems, PPE, proper ventilation, and effective emergency response plans, industries can mitigate risks associated with ammonia and create safer working environments. Vigilance, education, and adherence to best practices are key elements in safeguarding against the potential hazards of ammonia gas exposure.
MSA can help you set up a comprehensive ammonia safety plan for your facility. Visit our Ammonia Gas Detection Resource page for important information on ammonia safety, including an overview of available gas sensing technologies and safety solutions from MSA, compliance standards, select exposure limits across the globe, and more.
Sources
- “Ammonia – Health Effects” – Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) (https://www.osha.gov/)
- “Emergency Response Guidebook” – U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) (https://www.phmsa.dot.gov/)